Volleyball is more than just a sport – it’s a dynamic and thrilling game enjoyed by millions worldwide. Whether it’s played on a sandy beach or in a state-of-the-art indoor arena, volleyball’s appeal lies in its fast pace, team spirit, and accessibility. For players, coaches, and fans alike, understanding the dimensions of the court is essential. Knowing the measurements is not only important for setting up an official game but also plays a vital role in strategizing and ensuring fair play.
In this article, we’ll break down the exact dimensions of a volleyball court, including specific measurements for both indoor and outdoor play, as well as key features like the net, boundary lines, and attack zones. By the end, you’ll have a complete understanding of how the court is designed to accommodate this globally celebrated sport.
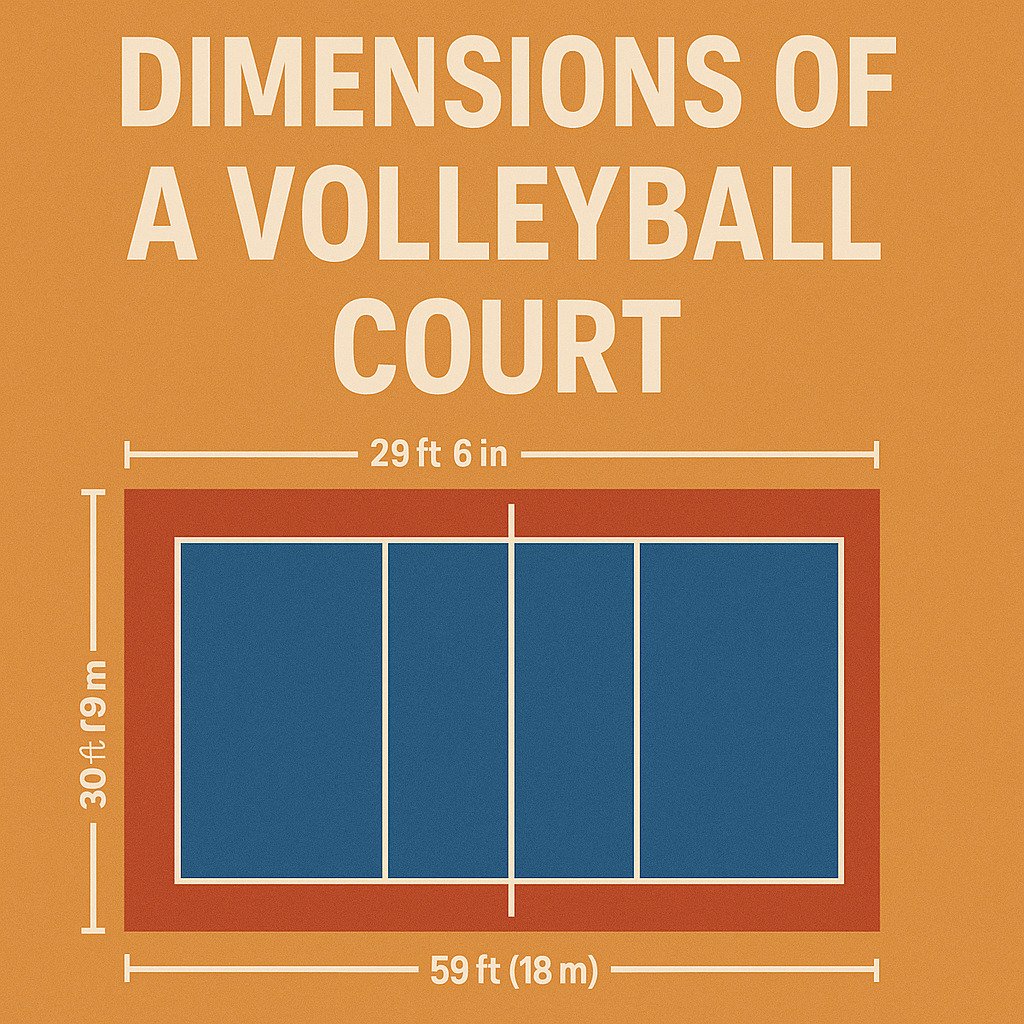
Standard Volleyball Court Dimensions
When it comes to volleyball, the court’s dimensions are as crucial as the gameplay itself. Whether you’re practicing indoors or enjoying a beach volleyball match, the court’s size sets the stage for fair and consistent play. Below, we break down the standard measurements for both indoor and outdoor volleyball courts, along with their distinguishing features.
Indoor Volleyball Court Dimensions
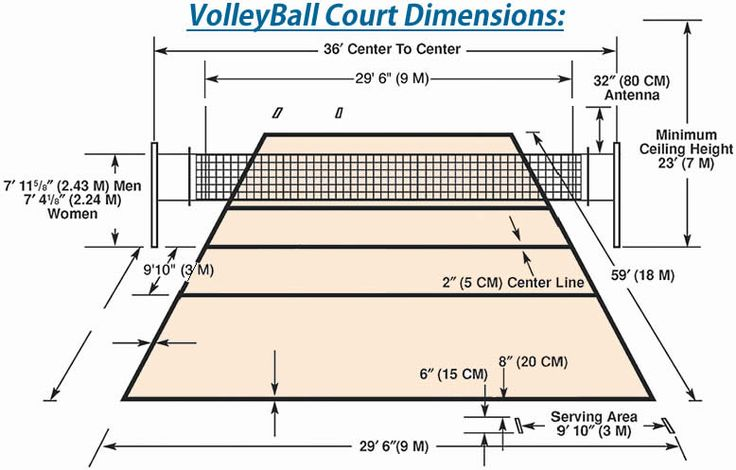
Indoor volleyball courts are designed with precise measurements to ensure uniformity across competitions worldwide. The court measures 18 meters (59 feet) in length and 9 meters (29.5 feet) in width. This rectangular space is divided into two equal halves by the centerline, with each side measuring 9 meters by 9 meters.
Key features of an indoor court include:
- Centerline – This line divides the court into two equal sides and is located directly beneath the net.
- Attack Line – Situated 3 meters (approximately 10 feet) from the centerline on both sides of the court. This line marks the area within which front-row players can perform offensive actions, such as attacking the ball above the net.
The clearly marked boundaries ensure all measurements are consistent, which is vital for official matches and tournaments.
Outdoor/Beach Volleyball Court Dimensions
Beach volleyball courts, while similar in shape to indoor courts, have slightly smaller dimensions. A standard beach volleyball court measures 16 meters (52.5 feet) in length and 8 meters (26.2 feet) in width. Like the indoor court, the beach court is also divided into two equal halves, each measuring 8 meters by 8 meters.
Key differences between indoor and outdoor courts include:
- Smaller Size – The reduced dimensions create a more challenging playing field, requiring players to cover more ground with fewer teammates (only two players per team in beach volleyball).
- No Attack Line – Unlike indoor courts, beach volleyball courts do not have an attack line, allowing players to strike from any position.
- Sand Surface – The beach court surface adds an extra level of difficulty, influencing movements and tactics during gameplay.
By adhering to these standardized measurements, players across various environments benefit from a consistent and fair game structure, whether battling for victory on a polished indoor surface or in the sand under the sun.
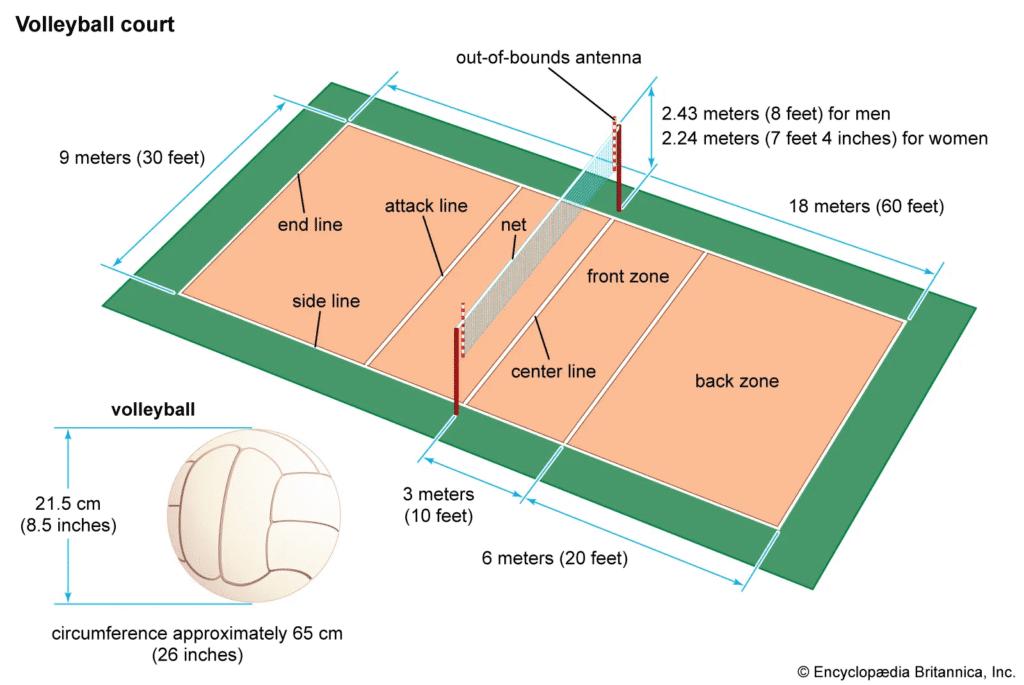
Net Height and Placement
The net in volleyball plays a crucial role in gameplay, acting as both a physical boundary and a strategic feature that requires players to perfect their skills in attack, defense, and blocking. Whether indoors or on the beach, the net’s height and placement are standardized to ensure consistency across all levels of play.
Standard Net Heights
The net height varies depending on the division of play, ensuring appropriate challenges for athletes of different categories. The standard heights are as follows:
- Men’s Net Height: 2.43 meters (7 feet 11 5/8 inches).
- Women’s Net Height: 2.24 meters (7 feet 4 1/8 inches).
These measurements are considered from the top of the net to the playing surface directly beneath it. For competitions involving mixed teams, the net is usually set at the men’s height unless otherwise specified by tournament rules.
Net Placement
The net is suspended horizontally over the centerline, dividing the court equally into two halves. It is tightly secured between two net posts, which are placed at an equal distance outside the sidelines. Proper net placement ensures:
- Tautness: The net should be stretched tight to maintain its height and prevent sagging during play.
- Centered Alignment: The middle of the net should align perfectly with the centerline, ensuring an even playing field.
The Role of Antennae
Attached to the net are two flexible rods called antennae, which significantly contribute to the game’s rules and fairness:
- Positioned vertically on either side of the net, above the sideline boundary.
- Extend 80 centimeters (31.5 inches) upward from the net.
- Serve as visible markers to determine whether the ball crosses within the boundaries of the court.
The ball must travel completely between the two antennae during play to be considered in bounds. This ensures clarity during high-speed rallies and allows for accurate officiating.
By maintaining precise net heights and correct placement, volleyball upholds its standard of fairness and competitiveness, ensuring that the equipment supports players in delivering their best performances.
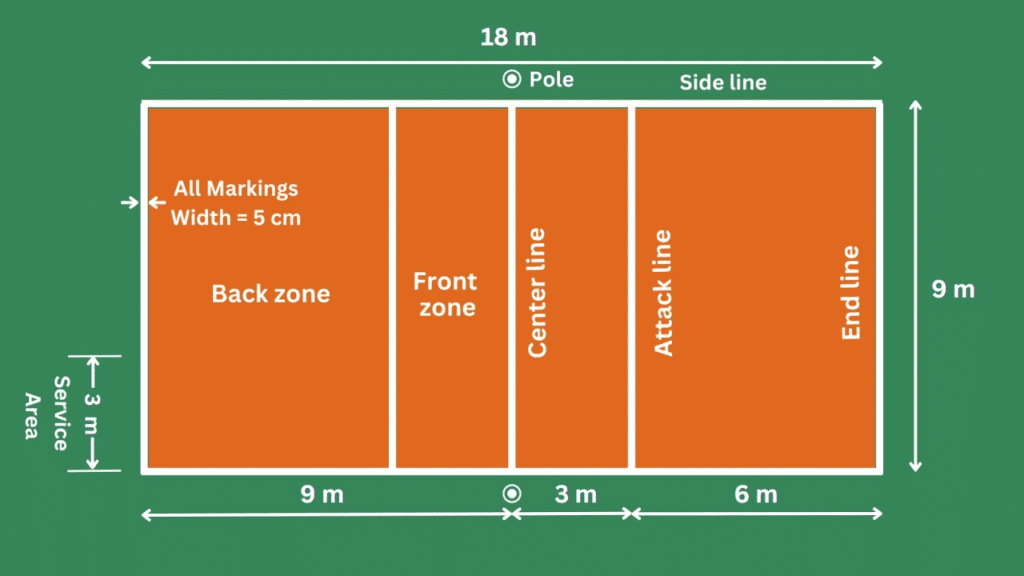
Boundary Lines and Zones
Understanding the boundary lines and zones of a volleyball court is fundamental for fair play and strategic success. Each line and zone on the court has a specific purpose and precise measurements, ensuring consistency in gameplay across all levels of competition. Below is a detailed breakdown of these critical court features.
Boundary Lines
The boundary lines define the playable area of the court and include the sidelines, end lines, and centerline.
- Sidelines:
These two lines run the length of the court on the left and right sides, measuring 18 meters (59 feet) for indoor courts and 16 meters (52.5 feet) for outdoor courts. The sidelines mark the lateral boundaries, and any ball landing outside these lines is considered out of play.
- End Lines:
Positioned at each end of the court, these lines mark the boundaries at the shorter ends of the rectangle. The distance between the two end lines is 9 meters (29.5 feet) for indoor courts and 8 meters (26.2 feet) for outdoor courts. They also serve as reference points for serving, with servers required to stand behind or on the end line when initiating play.
- Centerline:
The centerline divides the court into two equal halves, each 9 meters by 9 meters for indoor play or 8 meters by 8 meters for outdoor play. This line runs directly beneath the net and ensures a clear separation between opposing teams during gameplay.
Attack Line (3-Meter Line)
The attack line is a critical feature in indoor volleyball that adds a layer of strategy to the game. Situated 3 meters (approximately 10 feet) from the centerline on each side of the net, it marks the front and back zones of the court.
- Purpose:
The attack line indicates the area from which back-row players can perform offensive hits. These players must jump from behind the attack line when spiking the ball. This rule prevents overcrowding near the net and encourages strategic attacks from multiple court positions.
- Significance in Gameplay:
The attack line promotes dynamic play by requiring players to focus on positioning, timing, and precision when launching attacks from the backcourt. It also helps define player roles and the tactical setup of teams.
Free Zone
Surrounding the entire court is the free zone, an unmarked area that extends beyond the sidelines and end lines. The free zone typically measures 3 meters (10 feet) wide for indoor courts, but it can be larger in professional or international matches. For outdoor courts, the free zone often varies due to natural terrain.
- Function:
The free zone gives players room to chase and return balls that travel outside the court’s main boundaries. Successful rallies often involve players making extraordinary saves from within this area, adding excitement to the game.
Service Area
The service area is located behind the end line and spans the entire width of the court. For both indoor and outdoor play, this rectangular zone allows players flexibility when serving.
- Dimensions:
This area stretches 9 meters (29.5 feet) for indoor play or 8 meters (26.2 feet) for outdoor courts, matching the length of the end line.
- Purpose:
Players must serve the ball from within this area, ensuring they do not cross the end line before making contact with the ball. This rule guarantees consistency and allows opponents to anticipate the server’s position.
By adhering to the standardized dimensions and understanding the function of these boundary lines and zones, players and officials can maintain the integrity of volleyball matches while enhancing the competitive and strategic aspects of the game.
Court Surface and Markings
The surface and markings of a volleyball court play a pivotal role in ensuring smooth gameplay, player safety, and compliance with official standards. Whether indoors or outdoors, the court’s material and design must meet specific requirements to cater to the demands of this dynamic sport. Here’s a closer look at the materials and markings used, as well as the key safety considerations.
Indoor Volleyball Court Surfaces
Indoor volleyball courts are typically made of hardwood or synthetic materials, each offering unique benefits:
- Hardwood Surfaces:
- Maple wood is a common choice due to its durability and smooth finish.
- It provides excellent traction while allowing players to move freely without unnecessary resistance.
- Hardwood courts are usually coated with a protective finish to minimize wear and tear and maintain a polished appearance.
- Synthetic Surfaces:
- Made from materials like polyurethane or vinyl, these surfaces offer a cushioned feel, reducing impact on players’ joints.
- They are easy to maintain and provide consistent performance, making them a popular choice for multi-purpose sports halls.
The surface should be non-slip to reduce the risk of falls and injuries, while also being firm enough to support quick movements and jumps.
Outdoor Volleyball Court Surfaces
Outdoor volleyball courts, such as those used for beach volleyball, require completely different considerations:
- Sand Surface:
- Sand is the preferred material for outdoor courts, providing excellent cushioning and reducing the risk of injuries during dives or falls.
- The sand should be fine, clean, and free of debris to ensure safety and comfort for players.
- Proper leveling and consistent depth across the court are essential to avoid uneven surfaces that could lead to ankle or foot injuries.
Court Markings
Clear and visible markings are crucial for delineating boundaries and zones, ensuring fair play and facilitating accurate officiating. These include:
- Boundary Lines:
- Clearly define the playable area of the court, including the sidelines and end lines.
- Often made from contrasting colors to stand out against the court surface.
- Attack Lines:
- Marked 3 meters (10 feet) from the centerline in indoor courts to signify the area within which front-row players can execute attacks.
- These lines play a strategic role in defining player positioning and movement.
- Centerline:
- Positioned beneath the net to divide the court into two equal halves.
- Ensures that play is balanced and that both teams have equal court space.
High-quality markings are typically painted onto the surface or embedded in the material to prevent fading, ensuring they remain visible even after prolonged use.
Safety Considerations
Safety is a top priority when designing and maintaining volleyball courts. To minimize risks and support optimal performance, the following measures are essential:
- Non-Slip Surfaces:
- Indoor court materials should feature non-slip properties to reduce the risk of slipping during sudden movements.
- Regular cleaning and upkeep are necessary to maintain these properties over time.
- Regular Maintenance:
- Surfaces must be checked for damage, uneven areas, or worn markings. Repairs should be completed promptly to avoid hazards.
- Outdoor courts need frequent raking to level the sand and remove debris.
- Environmental Factors:
- For outdoor courts, adequate drainage systems should be in place to prevent waterlogging.
- Providing shade or covered areas can protect players from excessive sun exposure during long matches.
By ensuring that volleyball court surfaces and markings adhere to these standards, players can enjoy a safe, competitive, and consistent playing experience, whether practicing indoors on polished wood or competing outdoors in the sand.
Why Court Dimensions Matter
Standardized court dimensions are fundamental to the sport of volleyball, ensuring a consistent and fair environment for players, coaches, and officials across all levels of play. From recreational games to international tournaments, adhering to these dimensions is essential for maintaining the integrity of the game. Here’s why they matter.
Fairness and Consistency in Gameplay
One of the key reasons for standardized court dimensions is to provide a level playing field for all participants. When courts are built to the same specifications, players can rely on their skills and strategies without being influenced by varying court sizes. This consistency:
- Prevents any team from gaining an unfair advantage due to unfamiliar or improperly measured courts.
- Ensures that matches, especially in tournaments, follow uniform rules and conditions, enhancing the credibility of results.
Knowing the precise layout of the court allows players to execute their game plans effectively, whether it’s positioning for defense, setting up attacks, or serving accurately.
Influence on Player Strategy
The layout and dimensions of the volleyball court directly impact gameplay and team strategy. Players tailor their moves and tactics depending on the court’s boundaries, zones, and attack lines. For instance:
- Positioning and Spacing: Standardized dimensions help players master their spatial awareness, ensuring they’re optimally positioned during gameplay.
- Back and Front Zone Dynamics: The clearly marked attack line (3-meter line) dictates how teams divide their offensive and defensive responsibilities.
- Serving and Targeting: Accurately gauging the distance to the opposite end line influences serve placement and power, critical for point scoring.
Adhering to consistent court standards allows players to refine strategies that are effective regardless of where they play.
Impact on Training and Skill Development
Courts with standard dimensions provide a reliable training environment for players to hone their skills. Coaches can design drills and exercises with confidence that the techniques being practiced will translate effectively to official matches. For example:
- Players can develop precise serving, spiking, and blocking abilities calibrated to the court’s measurements.
- Teams can simulate game scenarios without needing adjustments or allowances for inconsistent court sizes.
- Familiarity with court zones promotes better decision-making and teamwork under competitive pressures.
Crucial for Officiating and Rule Enforcement
Standardized court dimensions are vital for referees and officials who oversee matches. With consistent measurements, officials can:
- Make clear and accurate judgments on plays, especially in determining whether a ball is in or out of bounds.
- Enforce rules related to zones and boundaries, minimizing disputes on whether actions like spikes or serves were legally executed.
Having a standardized playing area ensures fairness in officiating and reduces confusion during matches.
Essential for Official Matches and Tournaments
For official events, adhering to standard court dimensions is non-negotiable. These regulations ensure a professional and uniform playing experience, as all participants compete under identical conditions. This adherence:
- Facilitates smooth transitions for players competing at different venues during tournaments.
- Allows for fairness across various competitions, from regional championships to global events like the Olympics.
- Enhances spectators’ experience, as the consistent court setup reinforces the credibility of the sport.
Conclusion
The standardized dimensions of a volleyball court not only uphold the integrity of the game but also play a crucial role in shaping strategy, training, and officiating. By providing a uniform framework, they enable players and officials alike to focus on the skills, tactics, and moments that make volleyball the dynamic and exhilarating sport it is. Whether you’re watching a professional match or enjoying a casual game, these dimensions ensure that volleyball is a game everyone can play and enjoy on equal footing.
Tips for Setting Up a Volleyball Court

Setting up a volleyball court may seem straightforward, but achieving accurate measurements and a functional setup requires careful planning and attention to detail. Whether you’re preparing for a casual match or an official game, following these tips will ensure you create a precise and safe playing area.
Step 1: Measure the Court Accurately
Start by measuring the dimensions of the court based on its intended use. For indoor volleyball, the standard court size is 18 meters (59 feet) in length and 9 meters (29.5 feet) in width. For beach volleyball, the court is slightly smaller at 16 meters (52.5 feet) by 8 meters (26.2 feet).
- Tools You’ll Need:
- A measuring tape that is at least 20 meters (65 feet) long.
- Marker stakes or cones to outline the corners of the court.
- A string or rope for straight-line guides to keep edges even.
- How to Measure:
Step 2: Mark the Boundaries
Once the court dimensions are measured, mark the boundaries clearly. Use materials that are highly visible and durable.
- Boundary Marking Materials:
- Chalk or paint for temporary indoor surfaces.
- Court marking tape designed for gym floors.
- Rope, cord, or flexible plastic boundary lines for outdoor or beach setups.
- Tips for Marking:
- Ensure the boundary lines are at least 5 cm (2 inches) wide for visibility.
- For outdoor courts on grass or sand, secure the lines with stakes or anchors to prevent them from shifting during play.
Step 3: Set Up the Net
Installing the net over the centerline of the court is vital for proper gameplay. The net must be positioned at the correct height and tension.
- Equipment Needed:
- Regulation volleyball net.
- Sturdy poles or posts for securing the net.
- Adjustable straps or ropes to maintain net tension.
- How to Set It Up:
- Men’s Net Height: 2.43 meters (7 feet 11 5/8 inches).
- Women’s Net Height: 2.24 meters (7 feet 4 1/8 inches).
Step 4: Prepare the Free Zone and Service Area
A well-prepared free zone and service area are crucial for game flow and player movement.
- Free Zone:
- Extend at least 3 meters (10 feet) beyond the sidelines and end lines. Clear this space of obstacles to allow players to move freely.
- Service Area:
- Mark the area directly behind each end line, equal in width to the court itself. Ensure this space is flat and unobstructed to avoid distractions for servers.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Setting up a volleyball court requires thoroughness, so here are a few common pitfalls to watch out for:
- Uneven Surfaces:
- Incorrect Measurements:
- Weak Anchoring:
Final Thoughts
Setting up a volleyball court carefully guarantees a fair and enjoyable experience for players. By using the right tools, following standard measurements, and avoiding common mistakes, you can create a court that meets official standards and accommodates exciting gameplay. Take the time to set it up right, and both players and spectators will appreciate the effort you put into crafting the perfect volleyball environment.
FAQ’s
A standard indoor volleyball court measures 59 feet in length and 29.5 feet in width. This rectangle is divided into two equal halves by the centerline, with each side measuring 29.5 feet by 29.5 feet.
For outdoor or beach volleyball courts, the dimensions are slightly smaller, measuring 52.5 feet in length and 26.2 feet in width, with each half of the court being 26.2 feet by 26.2 feet.
Yes, beach volleyball courts are indeed smaller than indoor volleyball courts. While indoor courts measure 59 feet by 29.5 feet, beach volleyball courts are reduced to 52.5 feet by 26.2 feet. This reduction in size aligns with the format of beach volleyball, which typically features fewer players (two per team) compared to indoor volleyball (six per team). The smaller court size presents a greater challenge for players, who must cover more ground individually.
Yes, court dimensions may vary for recreational play, especially in informal or community settings. While official matches adhere strictly to standardized dimensions, players setting up a casual game might adjust the court size based on the available space or player preferences.
The net height in volleyball varies depending on the division of play:
Men’s Net Height: 7 feet 11 5/8 inches (2.43 meters).
Women’s Net Height: 7 feet 4 1/8 inches (2.24 meters).
Both measurements are taken from the top of the net to the playing surface directly beneath it. These heights ensure a suitable level of difficulty and competitiveness for players in their respective categories.